System based approach
Team work
Intensive exchange of information and knowledge
Efficient use of resources and elimination of losses
Continuous improvement

Method for system analysis of complex technical systems, using methods of technocenosis rank analysis, cluster analysis and interval estimation, as well as the latest intelligent technologies for processing large volumes of information, which allows to study potential for reducing the production cost, consisting of a large number of products, is developed especially for industrial companies in Uzbekistan. In this case final product cost includes cost of significant number of products included in its composition. Therefore, system analysis of potential of reducing the cost of production in a large enterprise is carried out in the system consisting of a factory and suppliers of components

The platform is designed for support corporate innovation process and aimed at organizations that are planning to collect and use ideas and suggestions of employees, as well as their customers to increase operational efficiency, improve the enterprise management system and sustainable development of the company in whole.
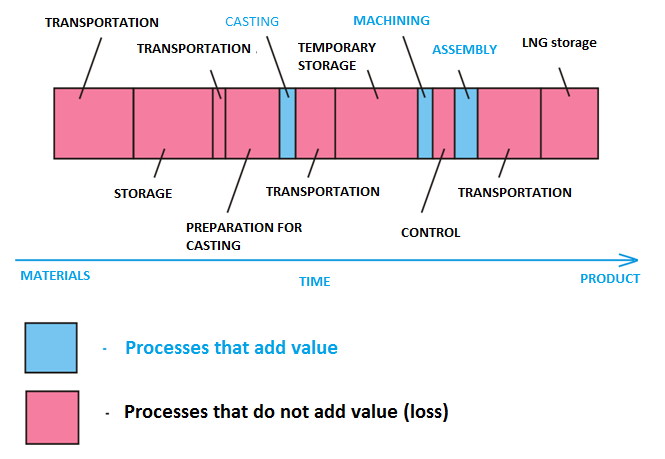
It is quite simple and intuitive graphic diagram showing material and information flows required to deliver product or service to the end user. Value stream map makes it possible to see the bottlenecks of the flow at once and identify, on its basis, all overheads and processes to develop a plan for improvement. Value stream – is all actions (value-adding and non-adding), needed to produce the product.
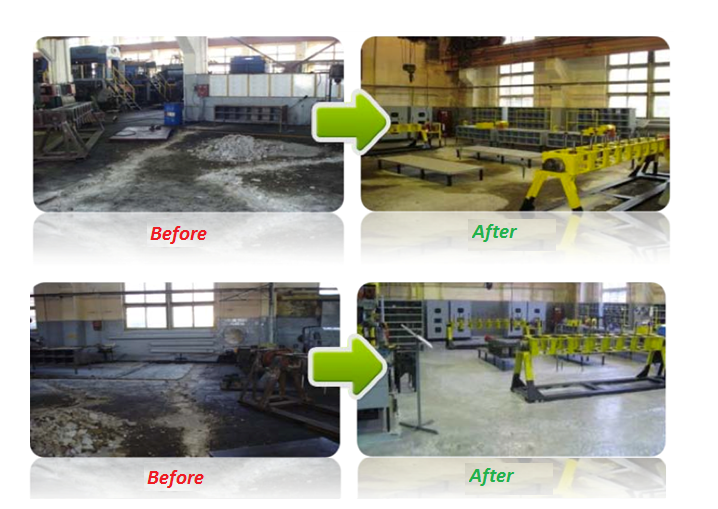

This method assumes organization of working space, taking into account creation of optimal conditions, cleanliness, neatness, order, time and energy saving. 5S System – is a technology for creating an effective workplace, which improves manageability of working area increasing culture of production and saving time. 5S system is a basic tool of lean production, that is, its introduction provides a base or foundation for further changes. In fact, the successful launch of 5S system provides a signal of willingness to further use of lean manufacturing tools.

The focus in this system is put on prevention and early detection of equipment defects that could lead to more serious problems. The basic idea of TPM is involvement in the process of equipment maintenance of all plant staff, and not only the corresponding teams. TPM implementation success, as well as of any other lean manufacturing instrument, is linked with the level of knowledge of the technique communicated to the staff and positively perceived by them. Use of TPM helps reduce losses associated with downtime due to breakdowns and excessive maintenance. The basis of TPM – is drawing up a preventive maintenance, lubrication, cleaning and general inspection schedule.

Visual management - is the location of all tools, parts, production steps and information on effectiveness of the production system in such way that they are clearly visible, and any participant of the process could assess the state of the system at first glance.

This document defines step-by-step sequence of any manufacturing operation. Verbal instructions are forgotten and deformed, so they have to be replaced by written SOP. SOP should not require a lot of time to understand, so visual notations, pictures, diagrams, photos, etc. should be used. SOP should be continuously updated, taking into account change in the order of operations. It is advised to attract employees in developing SOP, it guarantees its accuracy and acceptance.

It is the method of production organization, when materials or components from a previous operation (or from an external provider) are delivered at the moment when they are needed, and not beforehand. This system leads to a drastic reduction in the volume of work in progress, materials and finished goods in warehouses. "Just-in-time" system requires specific approach to selection and evaluation of suppliers, based on work with a narrow group of suppliers selected for their ability to guarantee "just- in-time" delivery of high quality components. At the same time, the number of suppliers is reduced by two times or more, and long-term business relations are established with the remaining suppliers.
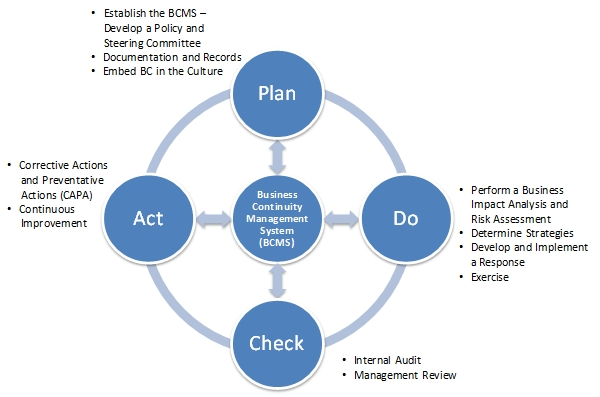
System of continuous improvement, also lean manufacturing, kaizen, etc. – is a philosophy or practice that is focused on continuous improvement of production processes, development of supporting business processes and management, as well as all aspects of the company’s and employees’ life. The concept of "continuous improvement" is a process of continuous improvements in the company, which are implemented by the employees of all ranks: by the workers at their workplaces and by the leaders in their processes. The process of "continuous improvement" can be graphically displayed as PDCA cycle. PDCA cycle – is abbreviation from "Plan-Do-Check-Act" cycle, also known as "Deming Cycle".
Efficient use of resources and elimination of losses
Involvement of staff in creative activity on the company's development
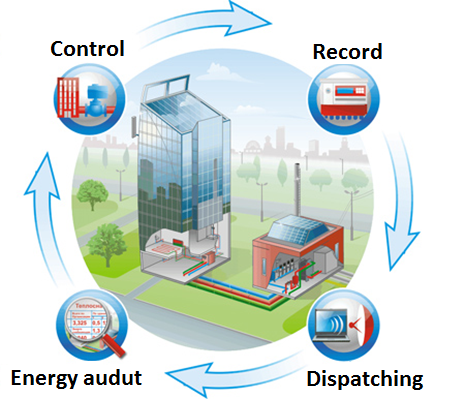
Determination of a subsystem with abnormal energy and material resources consumption, and personnel
Reduction of energy intensity of production and the share of energy costs in the production costs
Technology of creation of an effective workplace, which improves manageability of the working area, increases production culture and saves time
Intensive exchange of information and knowledge
Ability to identify nonproductive energy consumption and main reasons for its occurrence
Continuous improvement of production, management processes, and all aspects of the company’s and employees’ life
Reduction of losses associated with downtime due to breakdowns and extra maintenance
Method of production organization, when materials or components are delivered at the precise moment when they are needed